- The best Mini ITX PC cases of 2025: Expert recommended
- From Copilot to agent - AI is growing up, and CISOs need to be ready
- My favorite Apple Watch for tracking my workouts is 32% off at major retailers
- Discover the Cisco Catalyst Center Fundamentals (CCFND) Training Program
- This robot vacuum's dustbin doubles as a handheld vacuum (and it's on sale)
Microsoft’s January 2022 Patch Tuesday Addresses 97 CVEs (CVE-2022-21907)

Microsoft addresses 97 CVEs in its January 2022 Patch Tuesday release, including four zero-day vulnerabilities that were publicly disclosed but not exploited in the wild.
- 9Critical
- 88Important
- 0Moderate
- 0Low
Microsoft patched 97 CVEs in the December 2021 Patch Tuesday release, including nine rated as critical and 88 rated as important. Please note that Microsoft included patches for two CVEs in open source libraries.
This month’s update includes patches for:
- .NET Framework
- Microsoft Dynamics
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- Microsoft Exchange Server
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft Office Word
- Microsoft Teams
- Microsoft Windows Codecs Library
- Open Source Software
- Windows Hyper-V
- Tablet Windows User Interface
- Windows Account Control
- Windows Active Directory
- Windows AppContracts API Server
- Windows Application Model
- Windows BackupKey Remote Protocol
- Windows Bind Filter Driver
- Windows Certificates
- Windows Cleanup Manager
- Windows Clipboard User Service
- Windows Cluster Port Driver
- Windows Common Log File System Driver
- Windows Connected Devices Platform Service
- Windows Cryptographic Services
- Windows Defender
- Windows Devices Human Interface
- Windows Diagnostic Hub
- Windows DirectX
- Windows DWM Core Library
- Windows Event Tracing
- Windows Geolocation Service
- Windows HTTP Protocol Stack
- Windows IKE Extension
- Windows Installer
- Windows Kerberos
- Windows Kernel
- Windows Libarchive
- Windows Local Security Authority
- Windows Local Security Authority Subsystem Service
- Windows Modern Execution Server
- Windows Push Notifications
- Windows RDP
- Windows Remote Access Connection Manager
- Windows Remote Desktop
- Windows Remote Procedure Call Runtime
- Windows Resilient File System (ReFS)
- Windows Secure Boot
- Windows Security Center
- Windows StateRepository API
- Windows Storage
- Windows Storage Spaces Controller
- Windows System Launcher
- Windows Task Flow Data Engine
- Windows Tile Data Repository
- Windows UEFI
- Windows UI Immersive Server
- Windows User Profile Service
- Windows User-mode Driver Framework
- Windows Virtual Machine IDE Drive
- Windows Win32K
- Windows Workstation Service Remote Protocol
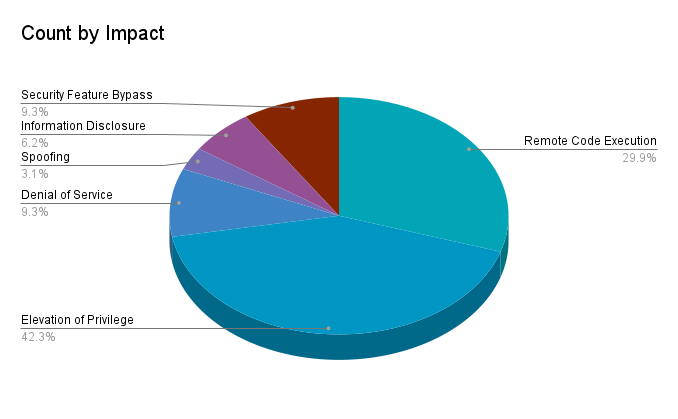
Elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities accounted for 42.3% of the vulnerabilities patched this month, followed by remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities at 29.9%.
CVE-2022-21907 | HTTP Protocol Stack Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21907 is a RCE vulnerability in Microsoft’s HTTP Protocol Stack (http.sys) that can be exploited by a remote, unauthenticated attacker by sending a crafted packet to an affected server. The vulnerability received a 9.8 CVSSv3 score and Microsoft warns that this flaw is considered wormable. Patching affected servers should be prioritized immediately. While the flaw has not been exploited, it was rated as “Exploitation More Likely” according to Microsoft’s Exploitability Index. According to the advisory, Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 version 1809 do not have the HTTP Trailer Support feature enabled by default, however this mitigation does not apply to other affected versions of Windows.
CVE-2022-21969, CVE-2022-21846 and CVE-21855 | Microsoft Exchange Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerabilities
CVE-2022-21969, CVE-2022-21846 and CVE-2022-21855 are RCEs in Microsoft Exchange Server that all received a CVSSv3 score of 9.0 and were rated as “Exploitation More Likely.” According to the advisories, these vulnerabilities require adjacent attack, meaning “it cannot simply be done across the internet, but instead needs something specific tied to the target.” The attacker would need to establish some sort of foothold in the target environment before exploiting these vulnerabilities.
CVE-2022-21969 is credited to Dr. Florian Hauser with Code White GmbH, CVE-2022-21855 was discovered by Andrew Ruddick from the Microsoft Security Response Center and CVE-2022-21846 is credited to the National Security Agency.
CVE-2022-21874 | Windows Security Center API Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21874 is a publicly disclosed RCE in the Windows Security Center API that received a CVSSv3 score of 7.8. It was discovered by Jinquan with DBAPPSecurity Lieying Lab. This vulnerability requires user interaction to exploit and the attack vector is local.
CVE-2022-21893 | Remote Desktop Protocol Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21893 is a RCE vulnerability in the Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP). In order to exploit this flaw, an attacker would need to convince a targeted user to connect to a malicious RDP server. Once an RDP connection has been established, the attacker could use the malicious RDP server to access or modify the contents of the clipboard and on the filesystem of the victim’s machine. While exploitation is less likely, the vulnerability is still an important flaw to remediate.
CVE-2022-21850 and CVE-2022-21851 | Remote Desktop Client Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21850 and CVE-2022-21851 are both RCE vulnerabilities in the Remote Desktop Client. For both CVEs, an attacker would need to convince a user on an affected version of the Remote Desktop Client to connect to a malicious RDP server. Each of these vulnerabilities received a CVSSv3 score of 8.8 and requires user interaction to exploit.
CVE-2022-21836 | Windows Certificate Spoofing Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21836 is a spoofing vulnerability affecting Windows certificates which has received a 7.8 CVSSv3 score. An attacker could utilize compromised certificates to bypass the Windows Platform Binary Table binary verification. While exploitation is rated as less likely, Microsoft states that the flaw was publicly disclosed. The compromised certificates known to Microsoft have been added to the Windows kernel driver block list and Microsoft offers additional guidance in their security advisory.
CVE-2022-21919 | Windows User Profile Service Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2022-21919 is an EoP vulnerability in the Windows User Profile Service. To exploit this vulnerability, an attacker would need to have established a foothold on the vulnerable system through social engineering, a separate exploit or malware. Successful exploitation would give an attacker elevated privileges on the vulnerable system. This vulnerability is considered a zero-day, as it was publicly disclosed prior to Microsoft issuing patches for it.
Internet Explorer 11 Upcoming End Of Life
Microsoft previously noted that support for Internet Explorer 11 will end on June 15, 2022 for certain versions of Windows 10. As some organizations may utilize applications that require the use of Internet Explorer, you will want to verify if you are using a long term supported version of Windows or determine next steps. Microsoft has provided an FAQ document here.
Tenable Solutions
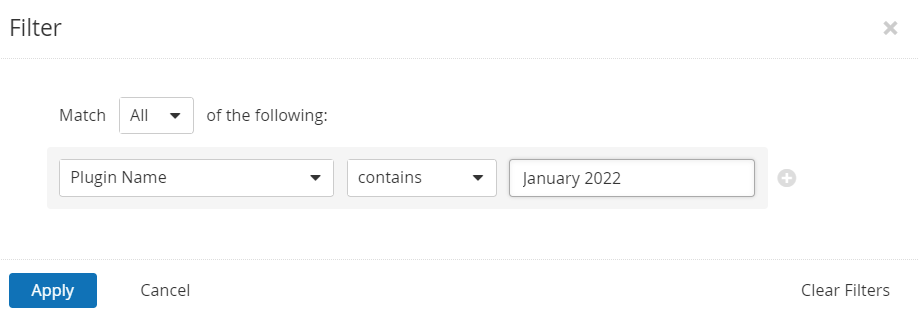
Users can create scans that focus specifically on our Patch Tuesday plugins. From a new advanced scan, in the plugins tab, set an advanced filter for Plugin Name contains January 2022.
With that filter set, click the plugin families to the left and enable each plugin that appears on the right side. Note: If your families on the left say Enabled, then all the plugins in that family are set. Disable the whole family before selecting the individual plugins for this scan. Here’s an example from Tenable.io:
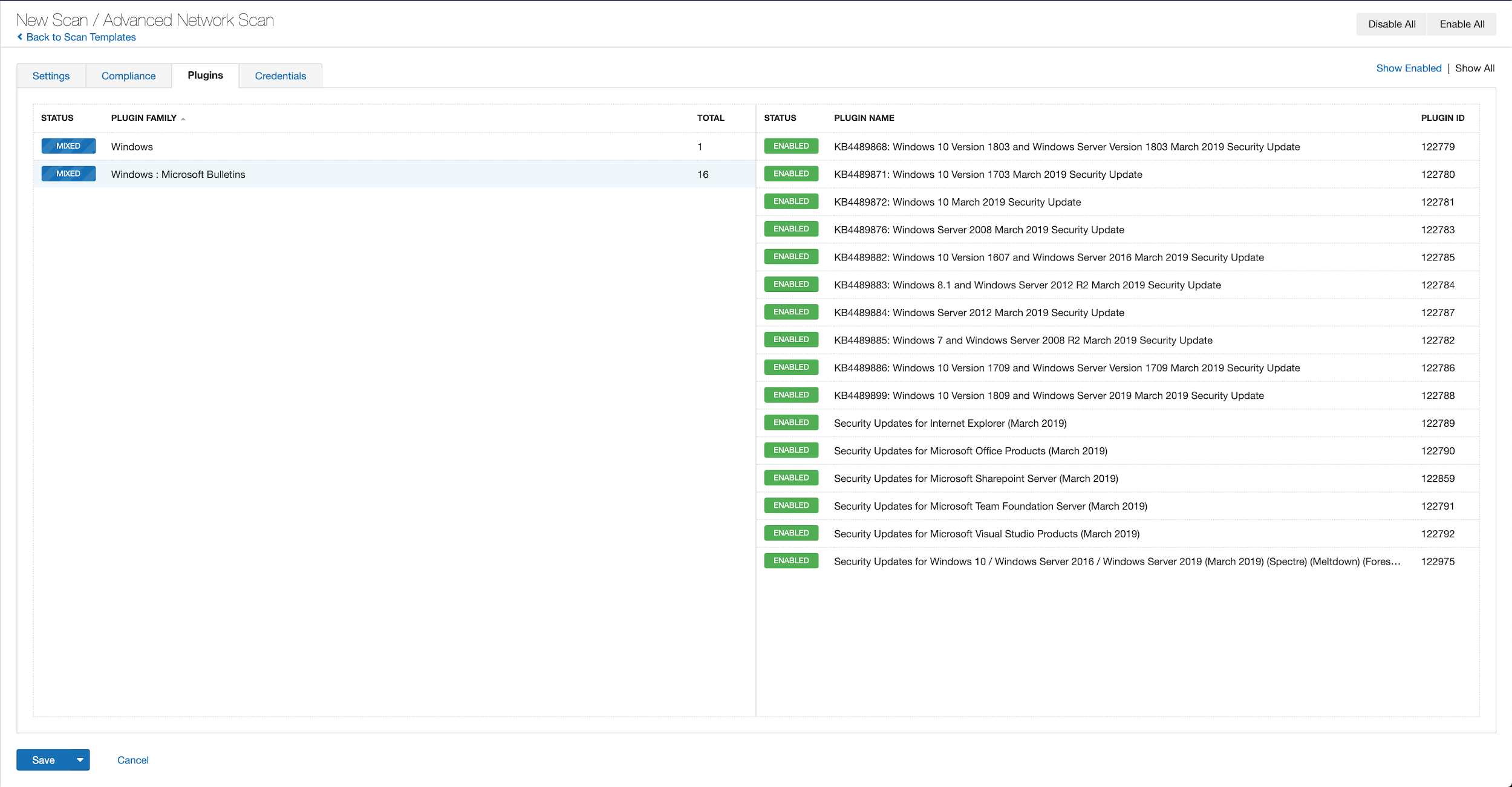
A list of all the plugins released for Tenable’s January 2022 Patch Tuesday update can be found here. As always, we recommend patching systems as soon as possible and regularly scanning your environment to identify those systems yet to be patched.
Get more information
Join Tenable’s Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable, the first Cyber Exposure platform for holistic management of your modern attack surface.
Get a free 30-day trial of Tenable.io Vulnerability Management.

