- Every dad should build their toolkit with theses 10 DIY gadgets
- Broadcom grows revenues by 20% following VMware purchase, as customers fume about subscription costs
- How global threat actors are weaponizing AI now, according to OpenAI
- The viral Air Purifier Table is my smart home's MVP (and it's on sale for $179)
- Grab the Galaxy S25 Edge for $170 off and get a free Amazon gift card - but act fast
Microsoft’s July 2022 Patch Tuesday Addresses 84 CVEs (CVE-2022-22047)

Microsoft addresses 84 CVEs in its July 2022 Patch Tuesday release, including four critical flaws and one zero day that has been exploited in the wild.
- 4Critical
- 79Important
- 0Moderate
- 0Low
Microsoft patched 84 CVEs in its July 2022 Patch Tuesday release, with four rated as critical, 79 rated as important and one rated as unknown..
This month’s update includes patches for:
- AMD CPU Branch
- Azure Site Recovery
- Azure Storage Library
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Office
- Open Source Software
- Role: DNS Server
- Role: Windows Fax Service
- Role: Windows Hyper-V
- Skype for Business and Microsoft Lync
- Windows Active Directory
- Windows Advanced Local Procedure Call
- Windows BitLocker
- Windows Boot Manager
- Windows Client/Server Runtime Subsystem
- Windows Connected Devices Platform Service
- Windows Credential Guard
- Windows Fast FAT Driver
- Windows Fax and Scan Service
- Windows Group Policy
- Windows IIS
- Windows Kernel
- Windows Media
- Windows Network File System
- Windows Performance Counters
- Windows Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol
- Windows Portable Device Enumerator Service
- Windows Print Spooler Components
- Windows Remote Procedure Call Runtime
- Windows Security Account Manager
- Windows Server Service
- Windows Shell
- Windows Storage
- XBox
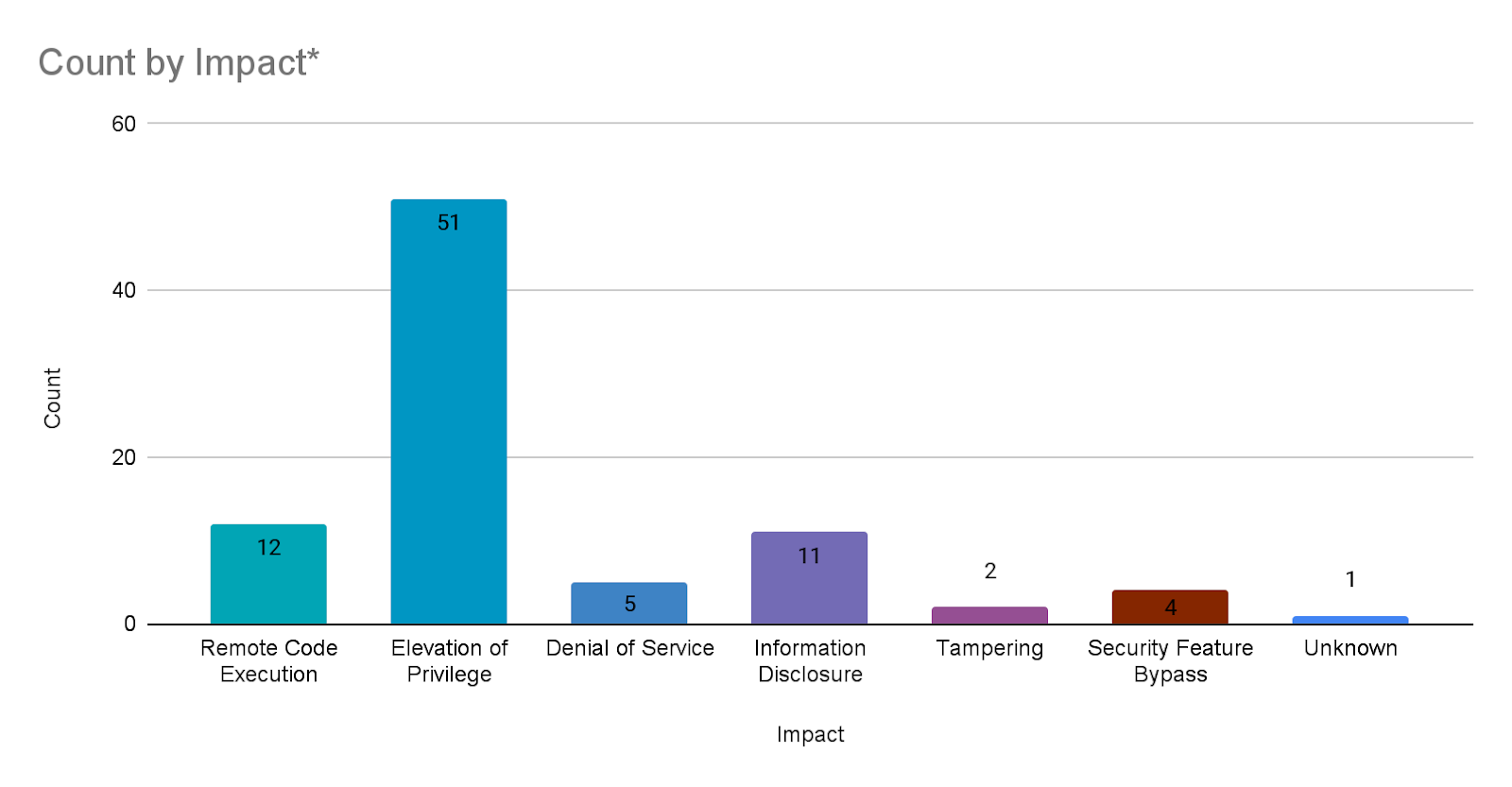
During most Patch Tuesday releases, Microsoft assigns a single impact for each CVE listed. However, in this month’s Patch Tuesday release, Microsoft assigned an additional impact for two CVEs, CVE-2022-22043 and CVE-2022-30225. As a result, we’ve counted these CVEs twice in the Count by Impact chart.
Elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities accounted for 59.3% of the vulnerabilities patched this month, followed by remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities at 14%.
CVE-2022-33675 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2022-33675 is a EoP vulnerability in Azure Site Recovery, a suite of tools aimed at providing disaster recovery services. The vulnerability was discovered and reported to Microsoft by Tenable researcher Jimi Sebree. It exists due to a directory permission error which can allow an attacker to use DLL hijacking to elevate their privileges to SYSTEM. You can read more about the discovery of the vulnerability on the Tenable Techblog and view our public advisory here.
Microsoft also patched several other vulnerabilities affecting Azure Site Recovery:
| CVE | Description | CVSSv3 |
|---|---|---|
| CVE-2022-33671 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33669 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33668 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33657 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33666 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33665 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33664 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33663 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33662 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33660 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33672 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33659 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33650 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33651 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33652 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.4 |
| CVE-2022-33653 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33654 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
| CVE-2022-33655 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33656 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33661 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33667 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33658 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.4 |
| CVE-2022-33641 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33673 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33674 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 8.3 |
| CVE-2022-30181 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33678 | Azure Site Recovery Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.2 |
| CVE-2022-33677 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 7.2 |
| CVE-2022-33676 | Azure Site Recovery Remote Code Execution Vulnerability | 7.2 |
| CVE-2022-33643 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 6.5 |
| CVE-2022-33642 | Azure Site Recovery Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | 4.9 |
CVE-2022-22047 | Windows CSRSS Elevation of Privilege
CVE-2022-22047 is an EoP vulnerability in the Windows Client Server Run-Time Subsystem. It received a CVSSv3 score of 7.8 and is rated as Important. Microsoft says this vulnerability has been exploited in the wild, though no further details have been shared at the time of publication. However, this type of vulnerability is likely to have been used as part of post-compromise activity, once an attacker has gained access to their targeted system and run a specially crafted application.
This vulnerability is credited to the Microsoft Threat Intelligence Center and Microsoft Security Response Center.
CVE-2022-22022, CVE-2022-22041, CVE-2022-30206, CVE-2022-30226 | Windows Print Spooler Elevation of Privilege Vulnerabilities
CVE-2022-22022, CVE-2022-22041, CVE-2022-30206 and CVE-2022-30226 are all EoP vulnerabilities in Windows Print Spooler components. After the deluge of vulnerability disclosures kicked off by PrintNightmare in August 2021, June 2022 was the first month in which Microsoft did not release any patches for Print Spooler. On balance, Microsoft has patched four high severity vulnerabilities in the service, all of which were rated “Exploitation Less Likely” based on Microsoft’s Exploitability Index. Three of the vulnerabilities were credited to researchers who disclosed Print Spooler flaws during the PrintNightmare saga last year. Xuefeng Li and Zhiniang Peng with Sangfor were the ones to kick it all off in late June 2021.
While the four vulnerabilities received somewhat similar CVSSv3 scores (listed in the table below), they grant attackers different levels of privilege escalation if exploited. CVE-2022-22022 and CVE-2022-30226 only allow an attacker to delete targeted files on a system while CVE-2022-22041 and CVE2022-30206 could grant an attacker SYSTEM privileges.
| CVE | Description | Acknowledgements | CVSS Score |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2022-22022 | Windows Print Spooler Elevation of Privilege | Xuefeng Li and Zhiniang Peng with Sangfor | 7.1 |
| CVE-2022-22041 | Windows Print Spooler Elevation of Privilege | JeongOh Kyea with Theori | 7.2 |
| CVE-2022-30206 | Windows Print Spooler Elevation of Privilege | Victor Mata with FusionX, Accenture Security and luckyu with NSFOCUS Tianyuan Lab | 7.8 |
| CVE-2022-30226 | Windows Print Spooler Elevation of Privilege | Xuefeng Li and Zhiniang Peng with Sangfor | 7.1 |
If patching is not feasible at this time, all four vulnerabilities can be mitigated by disabling the Print Spooler service. Microsoft’s advisories include PowerShell commands to do so.
CVE-2022-22038 | Remote Procedure Call Runtime Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2022-22038 is a RCE vulnerability in the Remote Procedure Call Runtime impacting all supported versions of Windows. The vulnerability received a CVSSv3 score of 8.1 and, while no privileges are required, the CVSS score indicates the attack complexity is high. Microsoft further supports this with a note in the advisory stating that additional actions by an attacker are required in order to prepare a target for successful exploitation. This is one of four vulnerabilities credited to Yuki Chen of Cyber KunLun in this month’s release.
CVE-2022-22028, CVE-2022-20229, CVE-2022-22039 | Windows Network File System Vulnerabilities
CVE-2022-22028 is an information disclosure vulnerability, whileCVE-2022-22029 and CVE-2022-22039are RCE vulnerabilities in the Windows Network File System (NFS). All three flaws were assigned an “Exploitation Less Likely” because these flaws have high attack complexity. In the case of CVE-2022-22029, an attacker would need to “invest time in repeated exploitation attempts” by “sending constant or intermittent data.” Both CVE-2022-22028 and CVE-2022-22039 require an attacker to “win a race condition” in order to exploit these vulnerabilities.
Microsoft attributed these vulnerabilities to security researcher Yuki Chen of Cyber KunLun. This is the third month in a row that Chen has reported vulnerabilities in Windows NFS, though the previously patched flaws carried a higher criticality rating.
Tenable Solutions
Users can create scans that focus specifically on our Patch Tuesday plugins. From a new advanced scan, in the plugins tab, set an advanced filter for Plugin Name contains July 2022.
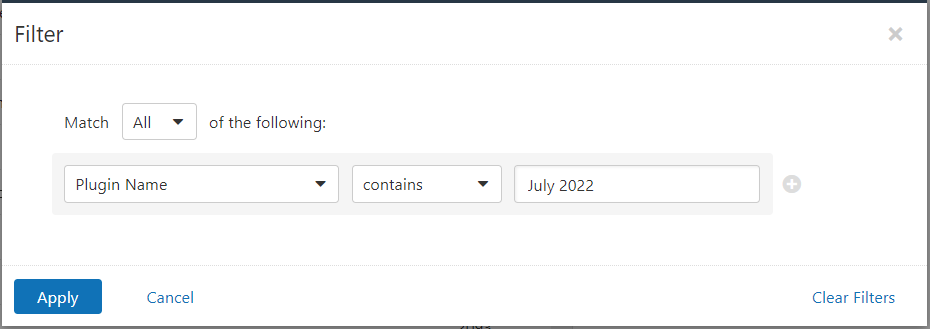
With that filter set, click the plugin families to the left and enable each plugin that appears on the right side. Note: If your families on the left say Enabled, then all the plugins in that family are set. Disable the whole family before selecting the individual plugins for this scan. Here’s an example from Tenable.io:
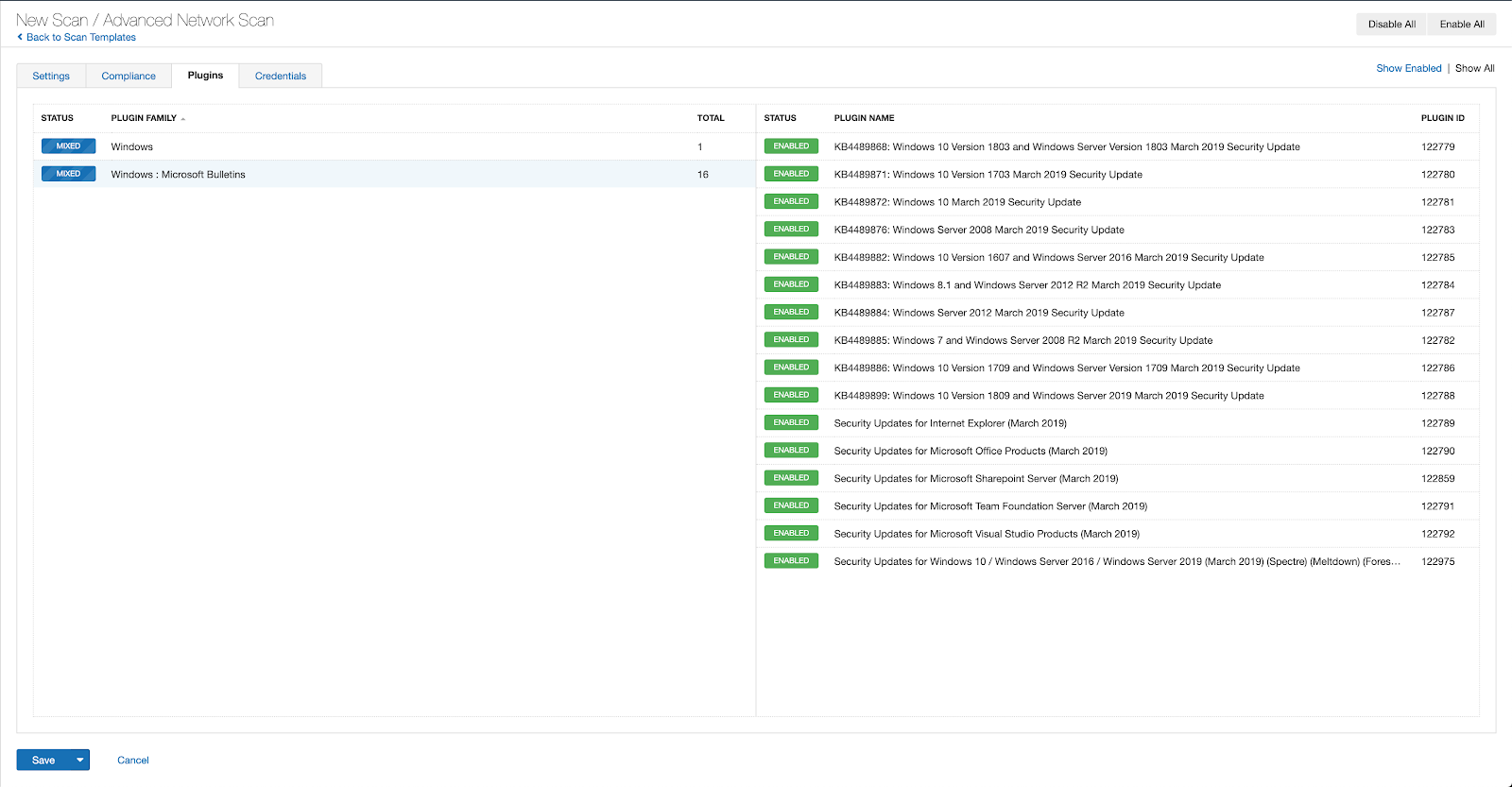
A list of all the plugins released for Tenable’s July 2022 Patch Tuesday update can be found here. As always, we recommend patching systems as soon as possible and regularly scanning your environment to identify those systems yet to be patched.
Get more information
Join Tenable’s Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable, the first Cyber Exposure platform for holistic management of your modern attack surface.
Get a free 30-day trial of Tenable.io Vulnerability Management.

