- ‘데이터브릭스 데이터+AI 서밋 2025’ 데이터 전문가를 위한 5가지 핵심 사항
- AI 아바타 시장 2032년까지 33.1% 성장 전망···마켓앤마켓, 개인화된 고객 경험 증가가 성장 견인
- Kali Linux gets a UI refresh, new tools, and an updated car hacking toolset
- How the Sandwich Generation Can Fight Back Against Scams | McAfee Blog
- Buy a Samsung Galaxy Watch 7 on sale and get a free SmartTag2 Bluetooth tracker - here's how
Microsoft’s February 2021 Patch Tuesday Addresses 56 CVEs (CVE-2021-24074, CVE-2021-24094, CVE-2021-24086)

Despite addressing only 56 CVEs, Microsoft’s February 2021 Patch Tuesday release contains fixes for a number of significant security threats, as well as an elevation of privilege vulnerability disclosed by Tenable’s Zero Day Research team.
Microsoft patched 56 CVEs in the February 2021 Patch Tuesday release, including 11 CVEs rated as critical and 43 rated as important.
This month’s Patch Tuesday release includes fixes for .NET Core, .NET Framework, Azure IoT, Developer Tools, Microsoft Azure Kubernetes Service, Microsoft Dynamics, Microsoft Edge for Android, Microsoft Exchange Server, Microsoft Graphics Component, Microsoft Office Excel, Microsoft Office SharePoint, Microsoft Windows Codecs Library, DNS Server, Hyper-V, Windows Fax Service, Skype for Business, SysInternals, System Center, Visual Studio, Windows Address Book, Windows Backup Engine, Windows Console Driver, Windows Defender, Windows DirectX, Windows Event Tracing, Windows Installer, Windows Kernel, Windows Mobile Device Management, Windows Network File System, Windows PFX Encryption, Windows PKU2U, Windows PowerShell, Windows Print Spooler Components, Windows Remote Procedure Call, Windows TCP/IP, and Windows Trust Verification API.
Remote code execution (RCE) vulnerabilities accounted for 37.5% of the vulnerabilities patched this month, followed by elevation of privilege (EoP) vulnerabilities at 21.4%.
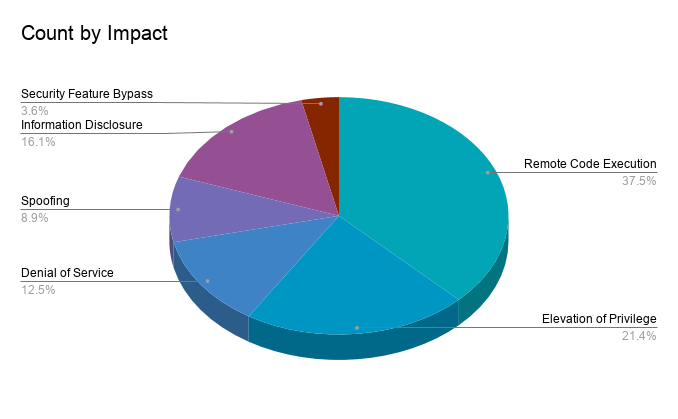
Despite the low number of CVEs patched this month, there are several significant patches included in this release.
CVE-2021-24074, CVE-2021-24094, and CVE-2021-24086 | Windows TCP/IP Vulnerabilities
CVE-2021-24074, CVE-2021-24094, and CVE-2021-24086 are a set of three vulnerabilities in Microsoft’s TCP/IP implementation for Windows.
| CVE | Impact | Severity | CVSSv3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| CVE-2021-24074 | Remote Code Execution | Critical | 9.8 |
| CVE-2021-24094 | Remote Code Execution | Critical | 9.8 |
| CVE-2021-24086 | Denial of Service | Important | 7.5 |
These vulnerabilities were discovered internally by Microsoft researchers. In a blog post detailing their findings, they explain why a functional exploit for the two critical RCE vulnerabilities will be “difficult” to create in the short term. However, they anticipate that exploits for the denial of service (DoS) flaw will be created “much more quickly” and should be expected soon after this release. They strongly encourage customers to apply these patches quickly.
Windows TCP/IP vulnerabilities:
– Internal find at Microsoft
– Not exploited in wild
– Exploit creation for RCE is very difficult
– Pre-patch workaround is deny Source Routing, which is disallowed by defaultCVE-2021-24074 CVE-2021-24094 CVE-2021-24086https://t.co/WJLhzqwRVp
— Kevin Beaumont (@GossiTheDog) February 9, 2021
If patching is not feasible at this time, Microsoft has provided a workaround that involves setting the Source Routing Behavior to “drop” requests. Microsoft notes that while IPv4 source routing is blocked by default in Windows, these requests are still processed. This configuration change ensures that the requests are not only dropped, but that they won’t even be processed.
Once patches have been applied, it is important to restore the setting back to its original state using the “dontforward” option.
CVE-2021-24078 | Windows DNS Server Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
CVE-2021-24078 is an RCE flaw within Windows server installations when configured as a DNS server. Affecting Windows Server versions from 2008 to 2019, including server core installations, this severe flaw is considered “more likely” to be exploited and received a CVSSv3 score of 9.8. This bug is exploitable by a remote attacker with no requirements for user interaction or a privileged account. As the vulnerability affects DNS servers, it is possible this flaw could be wormable and spread within a network.
CVE-2020-1472 | Netlogon Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2020-1472 is an EoP vulnerability in Windows Netlogon. Dubbed “Zerologon” by researchers at Secura, who discovered and disclosed the flaw, it was initially patched in Microsoft’s August 2020 Patch Tuesday release, the first of a two-part phased rollout. This month’s Patch Tuesday release contains the second and final patch. For more details about Zerologon, we released a companion blog post earlier today: Microsoft Finalizes Patch for Zerologon to Enable Enforcement Mode by Default.
CVE-2021-1732 | Windows Win32k Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2021-1732 is an EoP vulnerability due to the Windows kernel-mode driver improperly handling objects in memory. EoP vulnerabilities are often used post-compromise, since they require an attacker to first gain a foothold in a vulnerable system. Successful exploitation would elevate the privileges of an attacker, potentially allowing them to create new accounts, install programs, and view, modify or delete data. According to Microsoft, this vulnerability has been exploited in the wild. Kevin Beaumont, a security researcher at Microsoft, noted in a tweet that he worked on a threat analytics report about the vulnerability for Microsoft 365 customers.
I worked on a threat analytics report for Microsoft 365 customers on CVE-2021-1732, a zero day local elevation of privilege vulnerability in Win32k (patch out now). https://t.co/BHx92CVoUC
— Kevin Beaumont (@GossiTheDog) February 9, 2021
CVE-2021-1727 | Windows Installer Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2021-1727 is an EoP vulnerability found in the Windows Installer. According to the Microsoft advisory, this bug has been publicly disclosed and exploitation is considered “more likely.” In order to exploit this vulnerability, a local attacker would need a low-privileged user account, making this a likely candidate for inclusion as part of malicious software. Patches are available for Windows Server, Windows Server Core installations and non-server variants of all currently supported versions of Windows.
CVE-2021-1733 | Sysinternals PsExec Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
CVE-2021-1733 is an EoP vulnerability in PsExec, a Windows Sysinternals application used for remotely executing processes on systems within a network. The vulnerability was found and reported to Microsoft by David Wells, staff research engineer on Tenable’s Zero Day Research team. Wells wrote about the flaw on the Tenable Tech Blog and notes that “the local privilege escalation vulnerability could allow a non-admin process to escalate to SYSTEM if PsExec is executed locally or remotely on the target machine.” A proof-of-concept for the flaw has been added to the Tenable Github repository.
Tenable solutions
Users can create scans that focus specifically on our Patch Tuesday plugins. From a new advanced network scan, set an advanced filter for Plugin Name contains February 2021 in the plugins tab.
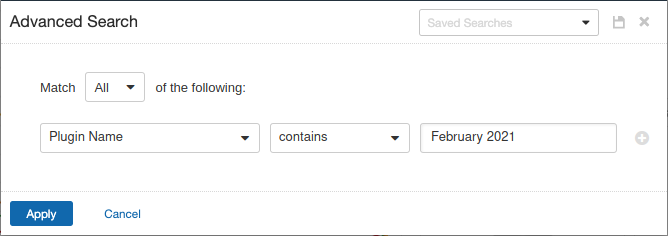
With that filter set, click the plugin families to the left and enable each plugin that appears on the right side. Note: If your families on the left say Enabled, then all the plugins in that family are set. Disable the whole family before selecting the individual plugins for this scan. Here’s an example from March 2019 using Tenable.io:
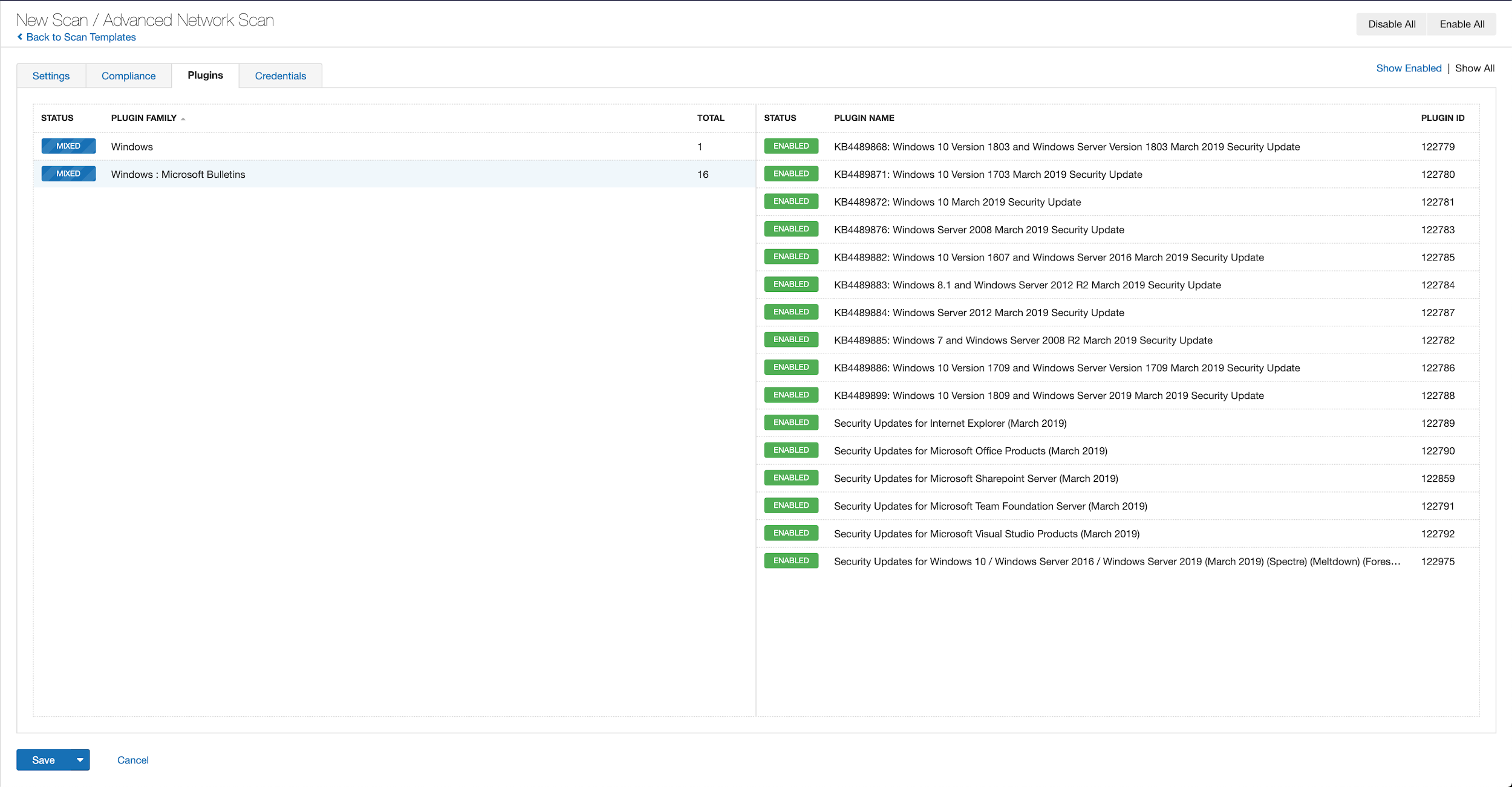
A list of all the plugins released for Tenable’s February 2021 Patch Tuesday update can be found here. As always, we recommend patching systems as soon as possible and regularly scanning your environment to identify those systems yet to be patched.
Get more information
Join Tenable’s Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable, the first Cyber Exposure platform for holistic management of your modern attack surface.
Get a free 30-day trial of Tenable.io Vulnerability Management.

