- Your iPad is getting a major upgrade for free. 4 top features I can't wait to try in iPadOS 26
- Your MacBook is getting a big upgrade. 5 best features I can't wait to use in MacOS 26
- The Growing Threat of AI-powered Cyberattacks in 2025
- I test tablets for a living and this is the Samsung tablet I recommend the most
- The Cost of Ignoring Patches: How State and Local Governments Can Mitigate Damaging Security Breaches
CVE-2020-27615: SQL Injection Vulnerability in WordPress Loginizer Plugin Affected Over One Million Sites

In a rare move, the WordPress Security Team forced a plugin update to over one million sites to address a vulnerability in a popular WordPress plugin used for brute force protection.
Background
On October 21, the developers of Loginizer, a popular WordPress plugin that offers protection against brute force attacks, published a blog post about a recent update to their plugin that addresses a severe vulnerability. The vulnerability was discovered and disclosed by a vulnerability researcher at WP Deeply, Slavco Mihajloski.
Analysis
CVE-2020-27615 is a SQL injection (SQLi) vulnerability in the WordPress Loginizer plugin due to a lack of input sanitization. According to a blog post from Mihajloski, the vulnerability exists in two parts of the Loginizer plugin: the loginizer_login_failed function, which contains unsanitized database requests, and the lz_valid_ip function. Mihajloski notes the potential for a stored cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerability as well.
An unauthenticated, remote attacker could exploit the vulnerability by crafting a malicious SQL query and including it in the username field of the WordPress site’s login page. Successful exploitation could lead to remote code execution.
Loginizer plugin has a history of vulnerabilities
This vulnerability isn’t the first to be reported in the Loginizer plugin. In 2017, researchers at WPSec published a blog post detailing their discovery of an SQLi and cross-site request forgery (CSRF) vulnerability, identified as CVE-2017-12650 and CVE-2017-12651 respectively.
In 2018, researcher and CEO of WPScan, Ryan Dewhurst, discovered and disclosed a stored XSS vulnerability in Loginizer. The vulnerability is identified as CVE-2018-11366.
WordPress Security team takes an unprecedented step to secure WordPress sites
It is not uncommon for researchers to uncover and disclose hundreds of vulnerabilities in WordPress plugins each year. However, according to a thread on the Loginizer Support Page, the WordPress Security team took an unprecedented step, swiftly addressing CVE-2020-27615 by using a “forced update” functionality in WordPress to migrate Loginizer users over to the patched version of the software. Apparently, this functionality has been present in WordPress for nearly seven years; it was introduced in WordPress version 3.7. According to Samuel Wood, a WordPress.org administrator, they have used this feature “many times.”
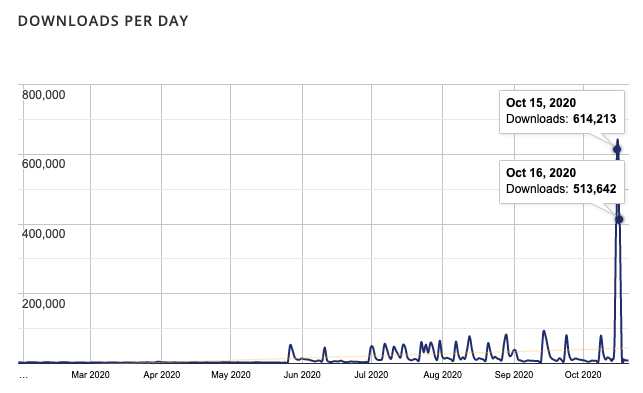
Image Source: WordPress Loginizer Plugin Statistics Page
On October 15 and 16, the Loginizer plugin saw a significant spike in downloads, being downloaded 1,127,855 times. This appears to be when the WordPress Security Team issued the forced update to the Loginizer plugin.
Proof of concept
Mihajloski published a proof of concept (PoC) for this vulnerability as part of his blog post.
Solution
The Loginizer developers patched this vulnerability in Loginizer version 1.6.4. Because WordPress has proactively forced updates to sites using the plugin, we expect many sites have already been patched. However, there still may be some sites out there that have not yet patched.
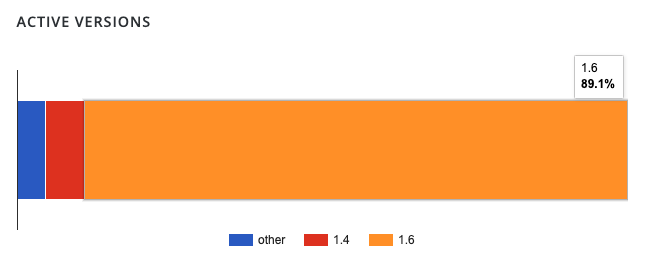
Image Source: WordPress Loginizer Plugin Statistics Page
The Loginizer statistics page on WordPress.org shows that 89% of sites running the plugin are on the 1.6.x branch. However, it’s unclear whether all of those sites on that branch are running 1.6.4. Almost 11% of Loginizer sites are using the 1.4.x branch or an unreported version of the branch. If your site has not been patched yet, we strongly advise you to upgrade to 1.6.4 immediately.
Identifying affected systems
A list of Tenable plugins to identify this vulnerability will appear here as they’re released. Additionally, vulnerable versions of Loginizer can be identified using our WordPress Outdated Plugin Detection plugin.
Get more information
Join Tenable’s Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable, the first Cyber Exposure platform for holistic management of your modern attack surface.
Get a free 30-day trial of Tenable.io Vulnerability Management.

