- 오픈AI, 아시아 4국에 데이터 레지던시 도입··· 한국 기업 데이터는 한국 서버에 저장
- Samsung confirms big durability upgrade for Galaxy S25 Edge - and it's mostly good news
- Dispute over Broadcom's licensing policy escalates
- Broadcom allegedly sends demand letters to perpetual VMware license holders
- The Nvidia Shield TV just got a long-awaited update - including these bug fixes
CVE-2024-47575: Frequently Asked Questions About FortiJump Zero-Day in FortiManager and FortiManager Cloud

Frequently asked questions about a zero-day vulnerability in Fortinet’s FortiManager that has reportedly been exploited in the wild.
Background
The Tenable Security Response Team (SRT) has compiled this blog to answer Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) regarding a zero-day vulnerability in Fortinet’s FortiManager.
Update October 23: The blog has been updated with new information about in-the-wild exploitation and threat actor activity associated with this vulnerability.
FAQ
What is FortiJump?
FortiJump is a name given to a zero-day vulnerability in the FortiGate-FortiManager (FGFM) protocol in Fortinet’s FortiManager and FortiManager Cloud. It was named by security researcher Kevin Beaumont in a blog post on October 22. Beaumont also created a logo for FortiJump.
What are the vulnerabilities associated with FortiJump?
On October 23, Fortinet published an advisory (FG-IR-24-423) for FortiJump, assigning a CVE identifier for the flaw.
| CVE | Description | CVSSv3 |
|---|---|---|
| CVE-2024-47575 | FortiManager Missing authentication in fgfmsd Vulnerability | 9.8 |
What is CVE-2024-47575?
CVE-2024-47575 is a missing authentication vulnerability in the FortiGate to FortiManager (FGFM) daemon (fgfmsd) in FortiManager and FortiManager Cloud.
How severe is CVE-2024-47575?
Exploitation of FortiJump could allow an unauthenticated, remote attacker using a valid FortiGate certificate to register unauthorized devices in FortiManager. Successful exploitation would grant the attacker the ability to view and modify files, such as configuration files, to obtain sensitive information, as well as the ability to manage other devices.
Obtaining a certificate from a FortiGate device is relatively easy:
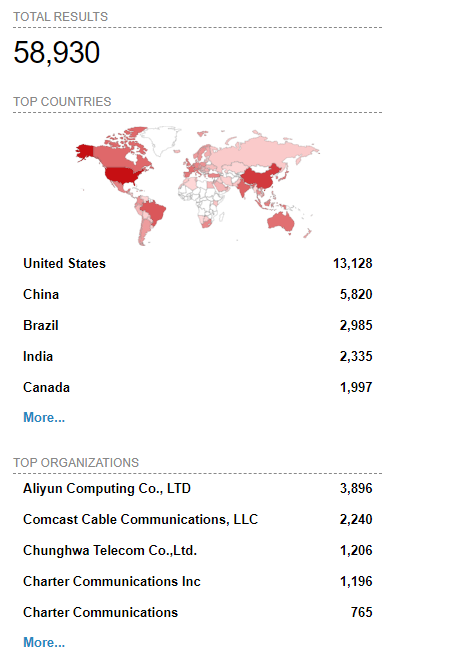
According to results from Shodan, there are nearly 60,000 FortiManager devices that are internet-facing, including over 13,000 in the United States, over 5,800 in China, nearly 3,000 in Brazil and 2,300 in India:
When was FortiJump first disclosed?
There were reports on Reddit that Fortinet proactively notified customers using FortiManager about the flaw ahead of the release of patches, though some customers say they never received any notifications. Beaumont posted a warning to Mastodon on October 13:
Was this exploited as a zero-day?
Yes, according to both Beaumont and Fortinet, FortiJump has been exploited in the wild as a zero-day. Additionally, Google Mandiant published a blog post on October 23 highlighting its collaborative investigation with Fortinet into the “mass exploitation” of this zero-day vulnerability. According to Google Mandiant, they’ve discovered over 50 plus “potentially compromised FortiManager devices in various industries.”
Which threat actors are exploiting FortiJump?
Google Mandiant attributed exploitation activity to a new threat cluster called UNC5820, adding that the cluster has been observed exploiting the flaw since “as early as June 27, 2024.”
Is there a proof-of-concept (PoC) available for this vulnerability/these vulnerabilities?
As of October 23, there are no public proof-of-concept exploits available for FortiJump.
Are patches or mitigations available for FortiJump?
The following table contains a list of affected products, versions and fixed versions.
| Affected Product | Affected Versions | Fixed Version |
|---|---|---|
| FortiManager 6.2 | 6.2.0 through 6.2.12 | Upgrade to 6.2.13 or above |
| FortiManager 6.4 | 6.4.0 through 6.4.14 | Upgrade to 6.4.15 or above |
| FortiManager 7.0 | 7.0.0 through 7.0.12 | Upgrade to 7.0.13 or above |
| FortiManager 7.2 | 7.2.0 through 7.2.7 | Upgrade to 7.2.8 or above |
| FortiManager 7.4 | 7.4.0 through 7.4.4 | Upgrade to 7.4.5 or above |
| FortiManager 7.6 | 7.6.0 | Upgrade to 7.6.1 or above |
| FortiManager Cloud 6.4 | 6.4 all versions | Migrate to a fixed release |
| FortiManager Cloud 7.0 | 7.0.1 through 7.0.12 | Upgrade to 7.0.13 or above |
| FortiManager Cloud 7.2 | 7.2.1 through 7.2.7 | Upgrade to 7.2.8 or above |
| FortiManager Cloud 7.4 | 7.4.1 through 7.4.4 | Upgrade to 7.4.5 or above |
| FortiManager Cloud 7.6 | Not affected | Not Applicable |
Fortinet’s advisory provides workarounds for specific impacted versions if patching is not feasible. These include blocking unknown devices from attempting to register to FortiManager, creating IP allow lists of approved FortiGate devices that can connect to FortiManager and the creation of custom certificates. Generally speaking, it is advised to ensure FGFM is not internet-facing.
Has Tenable released any product coverage for these vulnerabilities?
A list of Tenable plugins for this vulnerability can be found on the individual CVE page for CVE-2024-47575 as they’re released. This link will display all available plugins for this vulnerability, including upcoming plugins in our Plugins Pipeline.
Get more information
Change Log
Update October 23: The blog has been updated with new information about in-the-wild exploitation and threat actor activity associated with this vulnerability.
Join Tenable’s Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable One, the Exposure Management Platform for the modern attack surface.

