- El Capitan retains No. 1 supercomputer ranking
- Mexico’s Digital Growth Comes with Cybersecurity Challenges
- Apple just gave me a compelling reason to ditch my MacBook for an iPad. Here's why
- Wholesale Food Giant UNFI Admits Security Breach
- Remembering Bill Atkinson, the Apple visionary who invented MacPaint and changed the world
Manufacturing Top Targeted Industry in Record-Breaking Cyber Extortion

The year 2023 has been a record-breaking year for cyber extortion, according to Orange Cyberdefense (OCD).
The cybersecurity branch of the French internet service provider (ISP) launched its Security Navigator 2024 on November 30, 2023.
In this fifth edition of the firm’s annual threat landscape report, OCD saw that cyber extortion, the term used by the firm to refer to the compromise of some assets from a corporate network for ransom and includes ransomware, was the top threat faced by organization worldwide in 2023.
Although this was also the case last year, OCD also observed an unprecedented 46% increase in cyber extortion.
The manufacturing sector ranked as the top targeted industry, representing 20% of all cyber extortion campaigns (+42% compared with 2022 figures) and over 17% more than the second-placed industry, professional, scientific and technical services (+52%), OCD found.
Additionally, OCD saw a slight shift in geographical breakdowns of cyber extortion victims. Large, English-speaking economies continued to account for the highest numbers of victims, with over half (53%) headquartered in the US, followed by the UK (6%) and Canada (5%). However, OCD researchers are starting to see a lateralization of the geographic distribution, illustrated by significant year-on-year increases in victims in India (+97%), Oceania (+73%), and Africa (+70%).
Industry and Geographical Breakdowns of Cyber Incidents in 2023
Overall, OCD recorded 129,395 detected cyber incidents in 2023 – a 30% increase from 2022.
Among those, 25,076 were confirmed cyber incidents – a 14% drop compared with 2022. According to Wicus Ross, senior security researcher at OCD, this decrease is mainly due to their clients’ efficiency in dealing with these incidents.
“They have improved in how they deal with the volume of cyber incidents, and they have been able to automate their response more,” he said during a press conference held in London on November 29.
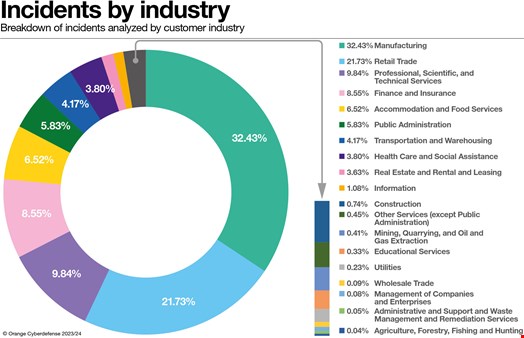
Again, the manufacturing sector was by far the largest contributor, accounting for 32.43% of the total of confirmed incidents, following the same pattern as in past years. The retail industry (21.73%) and professional, scientific and technological services (9.84%) completed the top three, responsible for over two-thirds of the confirmed incidents observed by OCD in 2023.
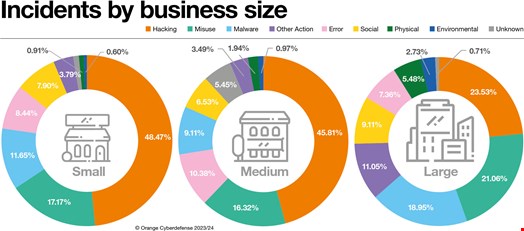
Large enterprises (250-10,000+ employees) have been impacted the most by cyber incidents in 2023, representing 40% of all attacks, followed by small organizations (25%) that employ 1 to 49 people.
Read about the previous edition of Orange Cyberdefense Security Navigator
Hacktivism, a Quickly Emerging Threat
Outside the domination of cyber extortion, one of the key takeaways from this year’s report shared by Ross during the launch event included an increasing blur between nation-state actors, cyber hacktivists and criminal actors.
Although OCD’s findings show that financially motivated threat actors are still overly dominant, with Lockbit 3.0, Clop, ALPHV/BlackCat, Paly and Royal ransomware groups representing 57% of detected cyber-attacks, hacktivist groups are emerging quicker than ever.
“Over the past two years, there has been an evident increase of activity in the hacktivism space to support causes of a political or social nature, […] such as the Russian war against Ukraine, with Ukraine, Poland and Sweden the most impacted by the pro-Russian hacktivists we track,” read the report.

“One interesting hacktivist group we’ve seen rise over the past year is Anonymous Sudan. Although new, they’ve been very vocal in their response regarding several events, conducting attacks against several countries, including Sweden and Denmark,” Ross said.
Although brand new, this group was observed by OCD as the second most active “pro-Russian hacktivist group” after NoName.
Read more: Growing Concern Over Role of Hacktivism in Israel-Hamas Conflict
What are Orange’s Cybersecurity Predictions for 2024?
Finally, the Security Navigator launch event allowed Olivier de Paillerets, recently appointed as OCD’s executive VP for technology and marketing, to share some of the firm’s security predictions for 2024.
These included the following:
- AI evolution: improved AI algorithms, driven by increased storage and computing capacities, will enhance both protection and attackers’ capabilities.
- Impact of laws and regulations: new regulations globally (e.g. SEC rules in the US, NIS2 directive in the EU) will shape cybersecurity practices, and sanctions and charges will elevate cybersecurity in boardrooms.
- Supplier consolidation: single vendor platforms or multi-vendor composable modules will gain prominence.
- Preparation for the quantum threat: a hybrid approach is recommended for protecting against quantum attacks.


