- Kali Linux gets a UI refresh, new tools, and an updated car hacking toolset
- How the Sandwich Generation Can Fight Back Against Scams | McAfee Blog
- Buy a Samsung Galaxy Watch 7 on sale and get a free SmartTag2 Bluetooth tracker - here's how
- Cisco capitalizes on Isovalent buy, unveils new load balancer
- I upgraded to Android 16 - here's what I love and what's still missing
Microsoft Patch Tuesday 2024 Year in Review

Microsoft addressed over 1000 CVEs as part of Patch Tuesday releases in 2024, including 22 zero-day vulnerabilities.
Background
Microsoft’s Patch Tuesday, a monthly release of software patches for Microsoft products, has just celebrated its 21st anniversary. After a wrap-up covering the 20th anniversary in 2023, the Tenable Security Response Team (SRT) chose to keep the tradition and cover trends and significant vulnerabilities from the 2024 Patch Tuesday releases.
Analysis
In 2024, Microsoft patched 1,009 CVEs throughout the year across a multitude of products. In contrast, 2023 saw 909 CVE’s patched and in 2022, 917 CVE’s were patched. While Microsoft has yet to break its 2020 record with 1,245 CVE’s patched, 2024 was still significant, as it is only the second time since Patch Tuesday’s inception that Microsoft patched over 1,000 CVE’s in a year.
Year over year, we see a steady increase in CVEs patched, with the exception of the outlier in 2020, a peak CVE count we have not yet seen matched.
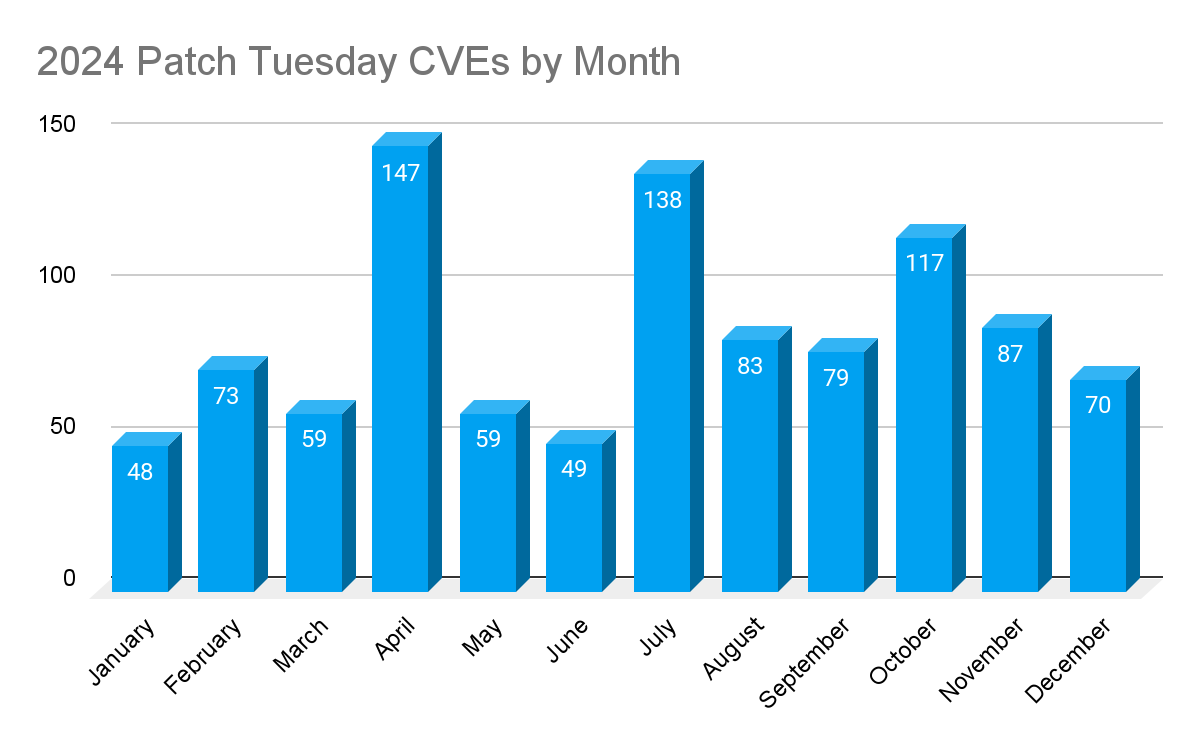
In 2024, the largest CVE count was observed in April, with Microsoft releasing patches for 147 CVEs. Only three months saw CVE counts over 100, with an average of 84 CVE’s patched per month.
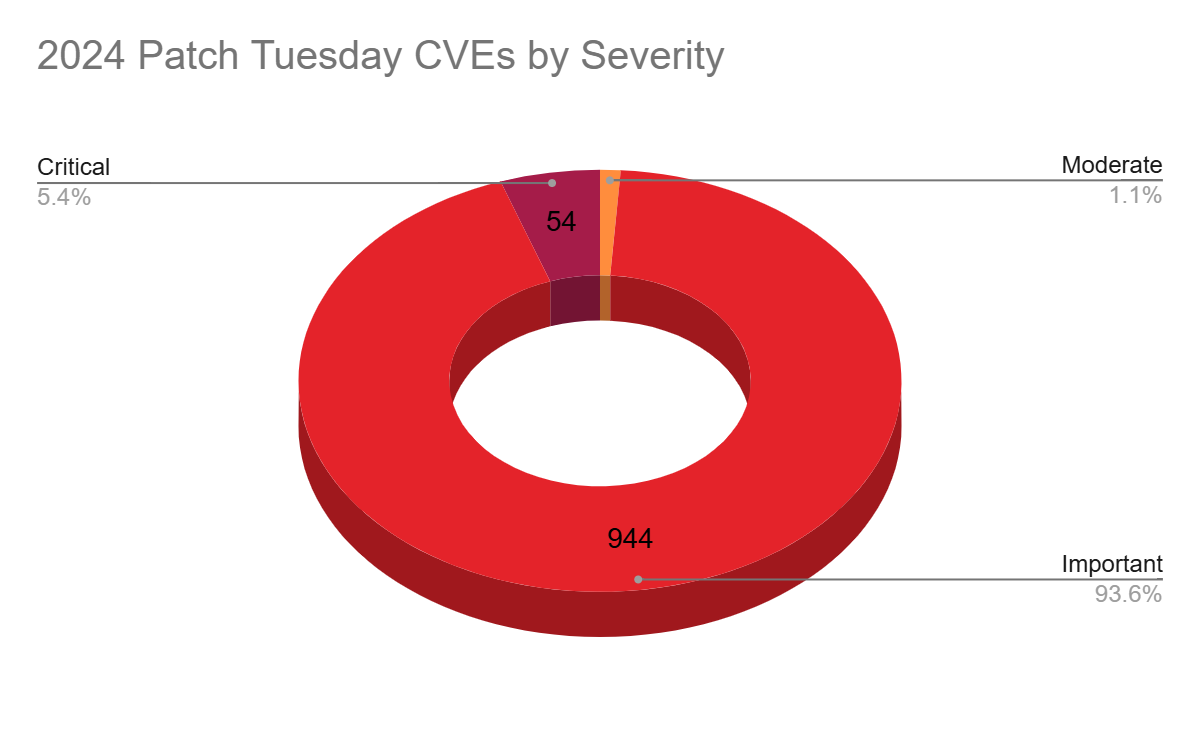
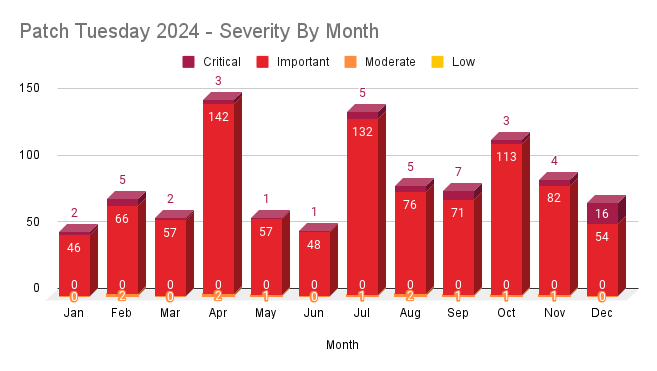
Patch Tuesday 2024 by severity
Each month, Microsoft categorizes vulnerabilities into four main severity levels: low, moderate, important and critical.
Just as in 2023, 2024 saw the majority of vulnerabilities rated as important, accounting for 93.6% of all CVEs patched, followed by critical at 5.4%. Moderate accounted for 1.1%, while there were no CVEs rated as low in 2024.
Patch Tuesday 2024 by impact
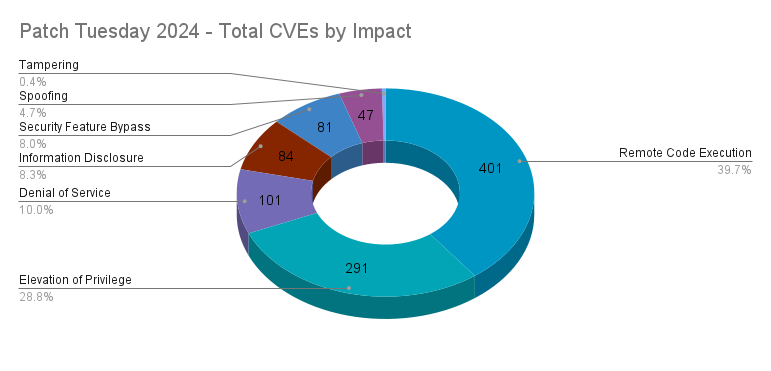
In addition to severity levels, Microsoft also categorizes vulnerabilities by seven impact levels: remote code execution (RCE), elevation of privilege (EoP), denial of service (DoS), information disclosure, spoofing, security feature bypass and tampering.
Once again in 2024, RCE vulnerabilities led the impact category, accounting for 39.7%, while EoP vulnerabilities accounted for 28.8%. DoS vulnerabilities ranked third, accounting for 10%, followed by information disclosure flaws at 8.3% and security feature bypass vulnerabilities at 8.0%. Last year, there were no vulnerabilities categorized as tampering, but this year, there were just four, which accounted for 0.4%.
Patch Tuesday 2024 zero-day vulnerabilities
According to Statista, Microsoft’s Windows operating system (OS) has a 72% market share as of February 2024, making it the most prominent OS. With the largest market share, Microsoft remains a top target for cybercriminals and advanced persistent threat (APT) groups. On occasion, these groups find and exploit vulnerabilities that remain unknown to Microsoft, known as zero-day vulnerabilities. Zero-day vulnerabilities are defined as vulnerabilities in software that have been exploited in the wild and/or have been publicly disclosed prior to patches becoming available. These zero-day vulnerabilities are often leveraged in limited, targeted attacks, however exploitation of these flaws can vary in depth and breadth.
In 2024, Microsoft patched 22 CVEs that were identified as zero-day vulnerabilities. Of the 22 zero-day vulnerabilities patched in 2024, 36.4% were EoP flaws. EoP vulnerabilities are often leveraged by APT actors and by determined cybercriminals seeking to elevate privileges as part of post-compromise activity. Following EoP flaws, security feature bypass vulnerabilities accounted for 27.3% of zero-days in 2024. While RCEs were the most prominent vulnerabilities across Patch Tuesday, they only accounted for 18.2% of zero-day flaws.
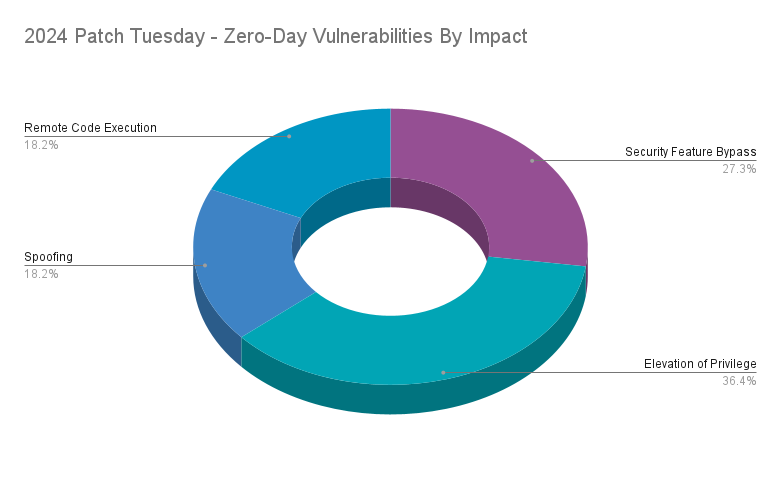
While these zero-days made up a small portion of the overall CVE’s addressed by Microsoft in 2024, we analyzed some of the most notable zero-day vulnerabilities of 2024. The table below includes these CVE’s with some details around their exploitation activity.
| CVE | Description | Exploitation Activity |
|---|---|---|
| CVE-2024-21338 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | Exploited by the Lazarus APT Group to deploy the FudModule rootkit |
| CVE-2024-21412 | Internet Shortcut Files Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | Water Hydra (aka DarkCasino) exploited this in a campaign named DarkGate. This APT has also exploited this CVE to deploy the DarkMe remote access trojan (RAT) |
| CVE-2024-30051 | Windows DWM Core Library Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | Used to deploy QakBot malware |
| CVE-2024-30088 | Windows Kernel Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | Exploited by APT34 (aka OilRig) |
| CVE-2024-38112 | Windows MSHTML Platform Spoofing Vulnerability | Exploited by APT group Void Banshee to deploy the malware known as Atlantida stealer. |
| CVE-2024-38178 | Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Vulnerability | Exploited by APT37 (aka RedEyes, Reaper, ScarCruft, Group123 and TA-RedAnt) |
| CVE-2024-38193 | Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | Exploited by the Lazarus APT Group (aka Diamond Sleet) to deploy the FudModule rootkit |
| CVE-2024-38213 | Windows Mark of the Web Security Feature Bypass Vulnerability | Water Hydra (aka DarkCasino) exploited this in a campaign named DarkGate. Vulnerability was named “Copy2Pwn” by Trend Micro’s Zero Day Initiative (ZDI) |
| CVE-2024-43451 | NTLM Hash Disclosure Spoofing Vulnerability | Exploited by APT known as UAC-0194 to deploy Spark RAT malware. |
| CVE-2024-43461 | Windows MSHTML Platform Spoofing Vulnerability | Exploited by APT group Void Banshee in an attack chain with CVE-2024-38112 |
| CVE-2024-49039 | Windows Task Scheduler Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability | Exploited by the threat actor tracked as RomCom to deploy the RomCom RAT malware. |
Conclusion
As we reflect on Patch Tuesday vulnerabilities in 2024, despite the year over year CVE counts being steady, we observed a small increase this year. While there will always be outliers, it is likely that 2025 will continue to follow an upward trend. In June, Microsoft announced that CVE’s would be issued for vulnerabilities in cloud-based products, even when no end user action is required. This could lead to a sharp increase in the number of CVEs assigned next year.
The SRT will continue to blog about Patch Tuesday each month along with other significant vulnerabilities that represent risk across the threat landscape, ensuring our readers are equipped with the most up to date information about the exposures that require immediate action.
Get more information
Join Tenable’s Security Response Team on the Tenable Community.
Learn more about Tenable One, the Exposure Management Platform for the modern attack surface.

