- You shouldn't trust AI for therapy - here's why
- How healthy is your home? Ultrahuman's newest device will tell you
- Google just spilled its airfare secrets: here's the cheapest day to book your next flight
- #Infosec2025: Top Six Cyber Trends CISOs Need to Know
- Stop chasing AI for AI’s sake
Molerats hackers deploy new malware in highly evasive campaign

The Palestinian-aligned APT group tracked as TA402 (aka Molerats) was spotted using a new implant named ‘NimbleMamba’ in a cyber-espionage campaign that leverages geofencing and URL redirects to legitimate websites.
The campaign was discovered by Proofpoint, whose analysts observed three variations of the infection chain, all targeting governments in Middle Eastern countries, foreign policy think tanks, and a state-owned airline.
As for the timeline of the recent attacks, the actors first used NimbleMamba in November 2021 and continued the operation until late January 2022.
Infection chain
In most attacks, TA402 uses spear-phishing emails that contain links to malware-dropping sites. The victims need to be within the targeted scope, or they are redirected to legitimate news sites.
If the target’s IP address matches the defined targeted region, a copy of NimbleMamba is dropped on their system inside a RAR file.
Proofpoint observed three different attach chains with slight variations concerning the theme of the phishing lure, the redirection URL, and the malware-hosting sites.
.jpg)
Source: Proofpoint
NimbleMamba
Proofpoint believes that TA402 developed NimbleMamba to replace LastConn, a backdoor and malware downloader exposed in a June 2021 report by the same firm.
In turn, LastConn is thought to have replaced SharpStage, exposed by Cybereason, in December 2020.
TA402 have demonstrated their capacity to quickly develop new custom tools when their existing set is uncovered and typically go through a period of distinct hiatus when they refresh.
NimbleMamba inevitably carries some code similarities with LastConn, but these are limited to the programming language, C2 encoding scheme, and the use of Dropbox API for communications.
The new tool features much more sophisticated anti-analysis systems and contains multiple guardrails to ensure that it only executes on targeted machines.
For example, the host needs to have the Arabic language pack installed, and the malware needs to be able to connect to four IP geolocation API services; otherwise, it won’t run.
If the prerequisites are met, NimbleMamba retrieves its configuration from a JustPaste.it page, which contains the obfuscated API auth key for C2 communication.
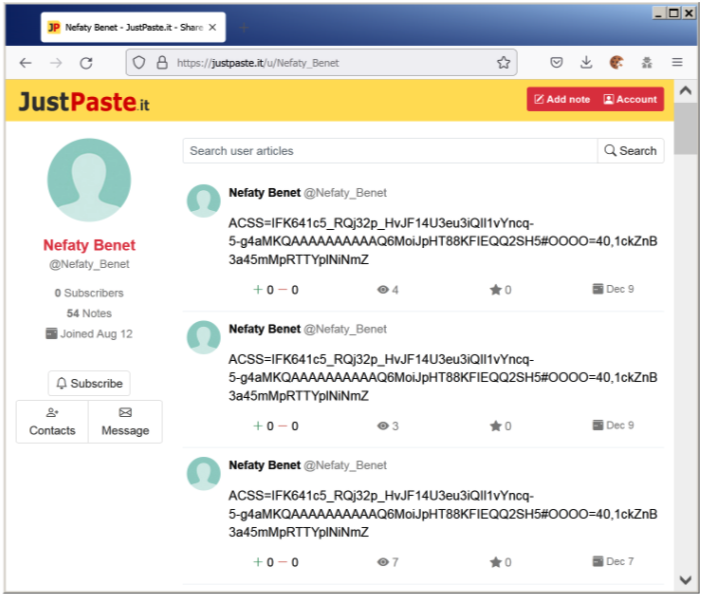
Source: Proofpoint
“NimbleMamba has the traditional capabilities of an intelligence-gathering trojan and is likely designed to be the initial access,” explains Proofpoint’s report.
“Functionalities include capturing screenshots and obtaining process information from the computer. Additionally, it can detect user interaction, such as looking for mouse movement.”
The RAR files fetched from Dropbox don’t always contain only NimbleMamba, as the analysts also retrieved the BrittleBush trojan, which is most likely used as a backup tool.
Outlook
Now that the refreshed toolset of TA402 has been exposed again, the actors are expected to go dormant for a while to develop new tools.
Already, the domains used for delivering NimbleMamba and C2 communications have been taken offline.
The critical thing to remember is that the particular actor maintains the same target focus, serves the same pro-Palestinian objectives, and uses mainly phishing emails to initiate the infection chain.

