- I recommend the Pixel 9 to most people looking to upgrade - especially while it's $250 off
- Google's viral research assistant just got its own app - here's how it can help you
- Sony will give you a free 55-inch 4K TV right now - but this is the last day to qualify
- I've used virtually every Linux distro, but this one has a fresh perspective
- The 7 gadgets I never travel without (and why they make such a big difference)
Why CISOs Are Looking to Lateral Security to Mitigate Ransomware

Findings from two eye-opening surveys conducted by VMware show that ransomware remains a top concern for enterprises worldwide. As IT and security leaders and chief information security officers (CISOs) look for answers, many are turning to deeper deployment and investment in lateral security tools.
What is lateral security? It leverages both access control and advanced threat prevention strategies and consists of a set of systematic, omnipresent tools deployed between the perimeter and endpoints. Key lateral security tools include:
- Network segmentation
- Micro-segmentation
- Advanced threat prevention capabilities such as intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS)
- Network sandboxes
- Network traffic analysis/network detection and response (NTA/NDR)
Ransomware By the Numbers
To understand the value of lateral security tools, it’s important to first assess the current state of ransomware. The number of attacks continues to grow unabated, with a 13% increase from 2020 to 2021—a larger increase than the previous five years combined.
This trend was echoed in a 2022 VMware survey of 200 IT and security leaders in North America, Europe, the Middle East, and Africa. Approximately one-third of the survey respondents work for a company with 1,001 to 5,000 employees, one-third represent companies with 5,001 to 10,000 employees, and one-third represent companies with more than 10,000 employees.
VMware
More than two-thirds (68%) of the respondents reported that their organization experienced at least one ransomware incident (whether successful or not) in the previous 24 months.
Of those reporting attacks, 42% said they suffered at least three incidents (whether successful or not). In addition to attacks on their own organizations, 55% of respondents are aware of three to six peer organizations that suffered at least one ransomware attack in the last 24 months.
Second Survey Focuses on Lessons Learned Following a Ransomware Attack
In a follow-up survey, VMware explored how security professionals whose organization experienced a ransomware incident in the last three years responded to the attack and what they changed in the aftermath. Isolating in on three core areas—people, process, and technology — the findings shed light on where security leaders believe they were underprepared and the steps they planned to take to address their gaps.
While most respondents reported their organizations had identity and access management and server endpoint protection/detection and response technologies in place before the ransomware incident, fewer had segmentation and advanced threat prevention tools deployed.

VMWare
Key Finding: The Flat Network
We interpret the findings on segmentation technologies to mean that a significant portion of the networks within respondents’ organizations was flat—including the area of the network that was hit by the ransomware. Flat networks provide no barrier against attackers that first compromise a lightly defended low-value system and then move laterally to infiltrate higher-value systems.
The bottom line is that network segmentation, micro-segmentation, and other essential lateral security tools were not deployed pervasively, leaving gaps in protection that attackers could exploit. It’s no surprise then that those organizations report an increase in interest in these types of tools after the ransomware incident.
Eliminating the Blind Spots with Lateral Security
As we all know, a successful ransomware attack can be devasting for companies, with an economic, operational, and reputational impact that requires extensive containment and recovery actions to restore systems and data.
Those IT and security leaders who are looking to improve their defenses are placing a sharper focus on the set of tools that make up lateral security. These technologies, when used in concert with each other, can eliminate the blind spots that prevent organizations from detecting threats as they move laterally through the infrastructure.
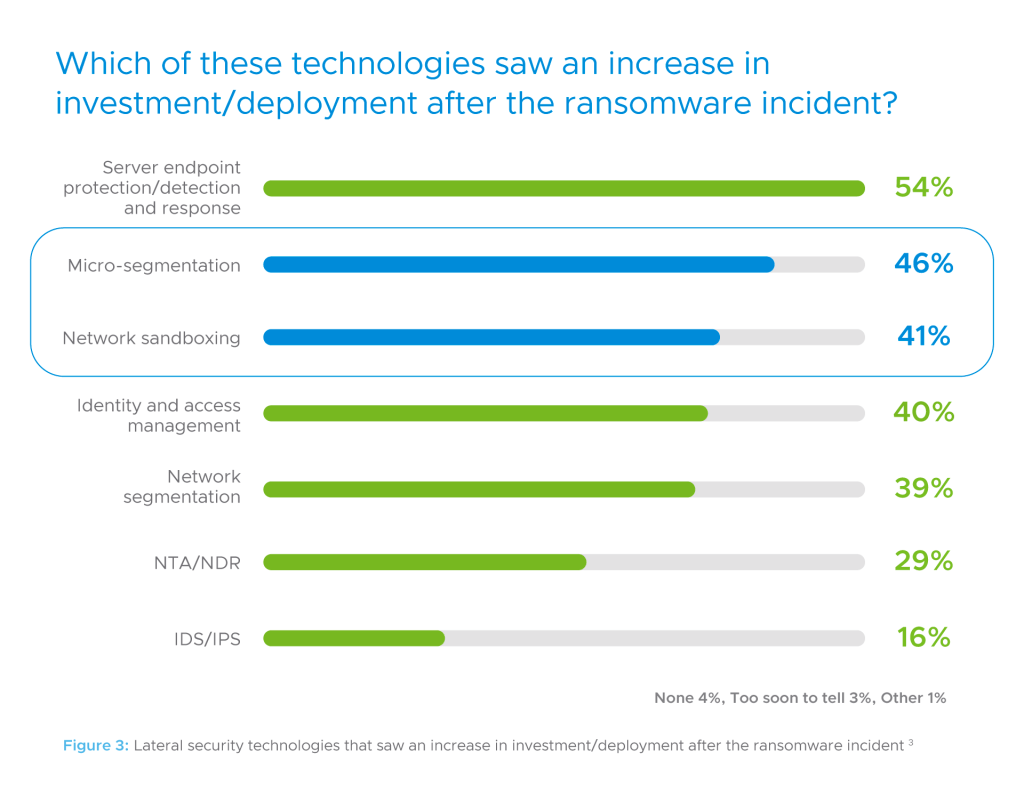
VMWare
Read our new white paper for a deeper dive into why and how CISOs and other IT and security leaders are deploying lateral security tools to effectively protect their organizations.
Click here to Learn more.

